What is “Neuropathy”?
Neuropathy is what happens when nerves start to become dysfunctional due to injury, disease or normal wear and tear. Medical practitioners can easily treat pain caused by any injury, such as a fracture or obvious inflammation resulting from active conditions such as rheumatoid arthritis. But what if there is a presence of pain that shows no sign of tissue damage or inflammation? Headaches, “whiplash”, backaches, tennis elbow or frozen shoulders, are all good examples of these conditions. “Neuropathic pain”, was first introduced by Dr. Gunn as a means of describing this type of condition. This can generally occur when nerves malfunction following some minor irritation. Nerves and nerve-endings may become extremely sensitive and cause subtle and sometimes harmless signals to become exaggerated, causing the false perception of pain. This characteristic is known medically as “denervation supersensitivity”. The result is pain -even while extensive medical examinations fail to isolate any specific problems. Until recently, supersensitivity had received little attention in the medical community. “Supersensitivity” and muscle shortening cannot be operated on and “cut away”.
The goal of treatment is to release muscle shortening which presses on and irritates the nerve. Supersensitive areas can be desensitized and the persistent pull of shortened muscles released with IMS.
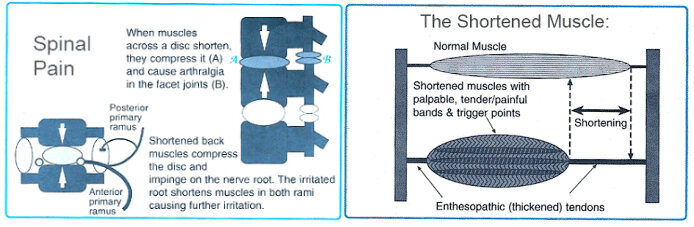
Shortened Muscle Syndrome
An important factor in neuropathic pain is muscle shortening, caused by muscle spasm and contracture. Muscle shortening produces pain by pulling on tendons, straining them as well as distressing the joints they move. Muscle shortening also increases wear and tear and contributes to degenerative changes such as “tendonitis” and “osteoarthritis”.
Involvement of the Spine
The most common cause of nerve irritation and neuropathic pain is “spondylosis”, degeneration in the spine, which can be the result of normal wear and tear. Spondylosis irritates the nerve root and leads to neuropathy and muscle shortening.